Deploying & Hosting in Firebase
— web-development, gatsbyjs, firebase, deployment — 6 min read
This is part of How i made this gatsby site series.
So far i have been repetitively doing designing, building and testing, right now i am at a stage to promote the changes to UAT and see the final build before implementation to perform this activity i will have to use gatsby build and finally get the site setup in Firebase to host.
# Final Stage of Testing
Source : Gatsby : Overview of the Gatsby Build Process
Gatsby builds everything ahead of time meaning it will complie all the assets like minifying css, javascript, transforming images, json files, etc. and saves them to public folder so when the site is run it doesn't need any server-side rendering. This is one of the features that makes Gatsby fast.
Run gatsby build to initiate the build process.
Output of the gatsby build
1PS D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv2> gatsby build2success open and validate gatsby-configs - 1.295s3success load plugins - 51.209s4success onPreInit - 0.160s5success delete html and css files from previous builds - 0.043s6success initialize cache - 0.055s7success copy gatsby files - 1.977s8success onPreBootstrap - 0.042s9success createSchemaCustomization - 0.084s10success source and transform nodes - 22.613s11success building schema - 1.737s12success createPages - 0.473s13success createPagesStatefully - 0.409s14success onPreExtractQueries - 0.024s15success update schema - 0.144s16success extract queries from components - 2.463s17success write out requires - 0.154s18success write out redirect data - 0.031s19success Build manifest and related icons - 0.131s20success onPostBootstrap - 0.348s21⠀22info bootstrap finished - 146.724 s23⠀24success Building production JavaScript and CSS bundles - 163.394s25success Rewriting compilation hashes - 0.076s26success run queries - 212.615s - 48/50 0.24/s27success Building static HTML for pages - 48.080s - 46/46 0.96/s28success Generating image thumbnails - 521.324s - 444/444 0.85/s29Generated public/sw.js, which will precache 9 files, totaling 413577 bytes.30success onPostBuild - 20.093s31info Done building in 663.339 secTest the output of the build compilation using gatsby serve
Output of gatsby serve
1PS D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv2> gatsby serve2info gatsby serve running at: http://localhost:9000/If everything looks good, you can signoff the UAT testing and proceed to deployment.
# Hosting in Firebase
Source : Deploying to Firebase Hosting
Steps below are pretty straight forward as in the above link,
Open firebase console using Google Account
Create a firebase project ( I already have a firebase project, mostly empty, so i am using that ). Click Project Overview and click Add App
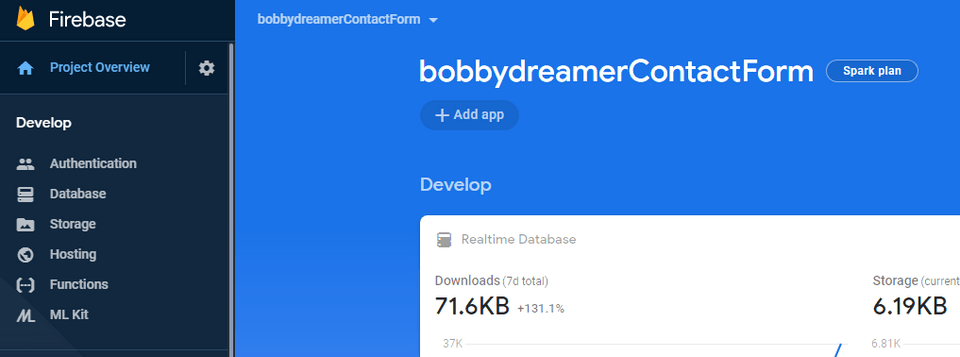
Also, i am thinking of change the project name from
bobbydreamerContactFormtobobbydreamer-siteas project-name seems to be editable in Settings.Click
</>icon
Fill in the details, App Nickname, Check Hosting and you have option either create new app or select existing one. I am selecting existing app and clicked Register App
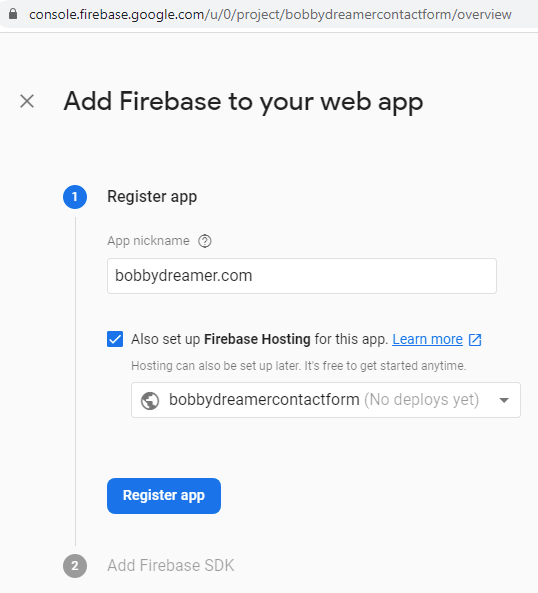
If you are building a Web Application, you should add this in the site. I am not using this at the moment. So, its not required for me.
Install firebase-tools, its needed to host your site with Firebase Hosting.
1npm install -g firebase-toolsAfter installation, go to the root folder of your site and sign into Firebase using Google account
1firebase loginTest the CLI using command
firebase projects:list1PS D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv2> firebase projects:list2√ Preparing the list of your Firebase projects3┌─────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────┬──────────────────────┐4│ Project Display Name │ Project ID │ Resource Location ID │5├─────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤6│ BTD-IN2-20180718 │ btd-in2-20180718 │ us-central │7├─────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤8│ feedbacks │ feedbacks-9be7f │ us-central │9├─────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤10│ stashit │ stashit-7885bob │ us-central │11├─────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤12│ bobbydreamerContactForm │ bobbydreamercontactform │ us-central │13├─────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤14│ API Project - 1 │ api-project-333122123186 │ us-central │15└─────────────────────────┴──────────────────────────┴──────────────────────┘16175 project(s) total.Run the below command in the root directory of your site to initialize Firebase this creates a
firebase.jsonconfiguration file which is required to deploy assets with the Firebase CLI because it specifies which files and settings from your project directory are deployed to your Firebase project.1firebase initNote: If you run
firebase initagain for any specific Firebase service, the command will overwrite the corresponding section of filefirebase.jsonback to the default configuration for that service.Below is the output of command
firebase init, have a look at the input and response of the highlighted code,1PS D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv2> firebase init23 ######## #### ######## ######## ######## ### ###### ########4 ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##5 ###### ## ######## ###### ######## ######### ###### ######6 ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##7 ## #### ## ## ######## ######## ## ## ###### ########89 You're about to initialize a Firebase project in this directory:1011 D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv21213 ? Are you ready to proceed? Yes14 ? Which Firebase CLI features do you want to set up for this folder? Press Space to select features, then Enter to confirm your choices. Hosting: Configure and deploy Firebase Hosting sites1516 === Project Setup1718 First, let's associate this project directory with a Firebase project.19 You can create multiple project aliases by running firebase use --add,20 but for now we'll just set up a default project.2122 ? Please select an option: Use an existing project23 ? Select a default Firebase project for this directory: bobbydreamercontactform (bobbydreamer-site)24 i Using project bobbydreamercontactform (bobbydreamer-site)2526 === Hosting Setup2728 Your public directory is the folder (relative to your project directory) that29 will contain Hosting assets to be uploaded with firebase deploy. If you30 have a build process for your assets, use your build's output directory.3132 ? What do you want to use as your public directory? public33 ? Configure as a single-page app (rewrite all urls to /index.html)? Yes34 ? File public/index.html already exists. Overwrite? No35 i Skipping write of public/index.html3637 i Writing configuration info to firebase.json...38 i Writing project information to .firebaserc...3940 + Firebase initialization complete!Replace
firebase.jsonwith below content1{2 "hosting": {3 "public": "public",4 "ignore": ["firebase.json", "**/.*", "**/node_modules/**"],5 "headers": [6 {7 "source": "**/*",8 "headers": [9 {10 "key": "cache-control",11 "value": "cache-control: public, max-age=0, must-revalidate"12 }13 ]14 },15 {16 "source": "static/**",17 "headers": [18 {19 "key": "cache-control",20 "value": "public, max-age=31536000, immutable"21 }22 ]23 },24 {25 "source": "**/*.@(css|js)",26 "headers": [27 {28 "key": "cache-control",29 "value": "public, max-age=31536000, immutable"30 }31 ]32 },33 {34 "source": "sw.js",35 "headers": [36 {37 "key": "cache-control",38 "value": "cache-control: public, max-age=0, must-revalidate"39 }40 ]41 },42 {43 "source": "page-data/**",44 "headers": [45 {46 "key": "cache-control",47 "value": "cache-control: public, max-age=0, must-revalidate"48 }49 ]50 }51 ]52 }53}Test the site from firebase perspective using command
firebase serve --only hosting. Just being careful as two technologies are involved here.1PS D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv2> firebase serve --only hosting2 i hosting: Serving hosting files from: public3 + hosting: Local server: http://localhost:50004 .......Deploy the site to firebase using below command and at the end of deployment you will get the site URL.
1firebase deploy -m "Initial Site"Output of
firebase deploy1PS D:\BigData\08. HTML\Gatsby\lupin\bdv2> firebase deploy -m "Initial Site"23 === Deploying to 'bobbydreamercontactform'...45 i deploying hosting6 i hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: beginning deploy...7 i hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: found 666 files in public8 + hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: file upload complete9 i hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: finalizing version...10 + hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: version finalized11 i hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: releasing new version...12 + hosting[bobbydreamercontactform]: release complete1314 + Deploy complete!1516 Project Console: https://console.firebase.google.com/project/bobbydreamercontactform/overview17 Hosting URL: https://bobbydreamercontactform.firebaseapp.comYou can the check deployment details in Firebase Console as well,
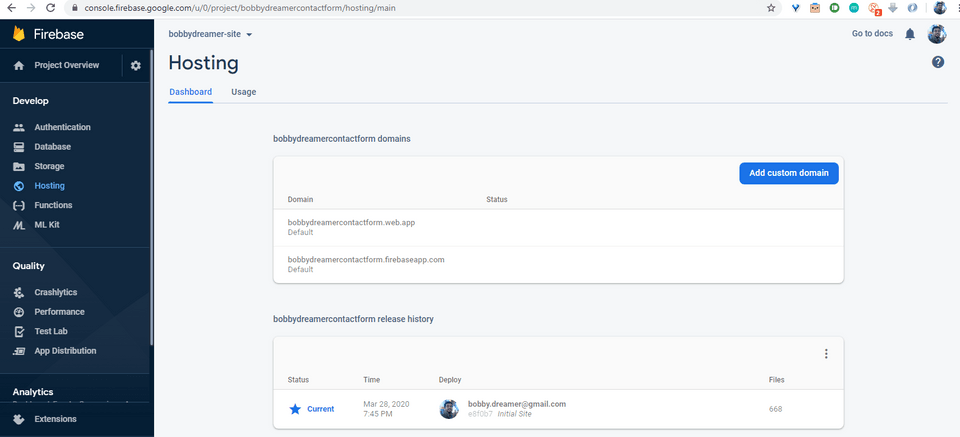
# Connecting to a custom domain
Source : Connect a custom domain
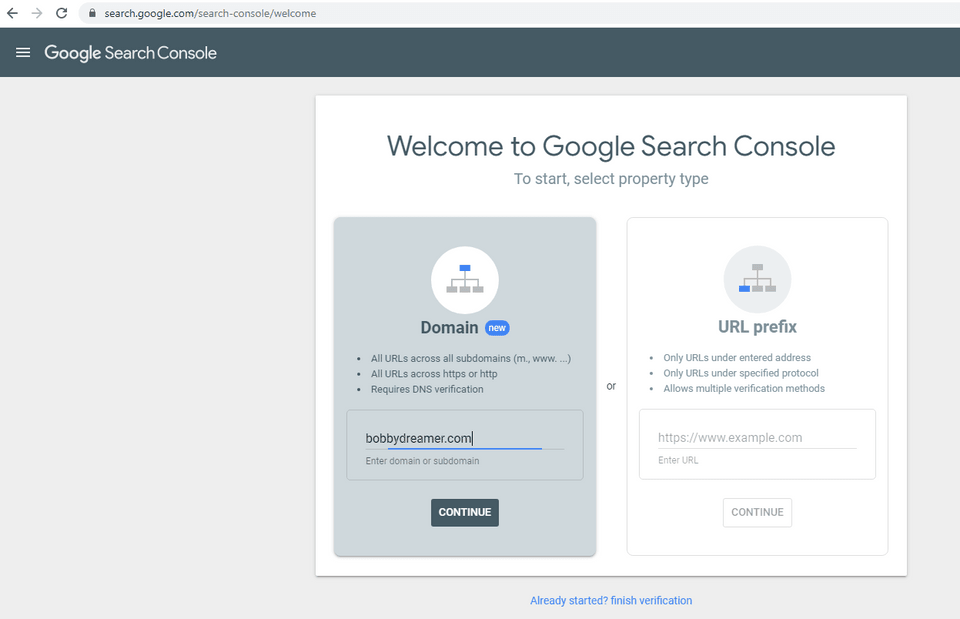
I have purchased a domain bobbydreamer.com using Google Domains and when setting up hosting there will be a process to verify ownership and to ease up that process, i am going to verify the ownership early by visiting Google Search Console, this doesn't take much time actually and along with that, it will setup an account for the website where you will have a dashboard view of site's performances and errors and many more. At this point, this Search Console dashboard is also new to me, so i am not going into it, at the moment.
Enter site name and click continue
Click Done
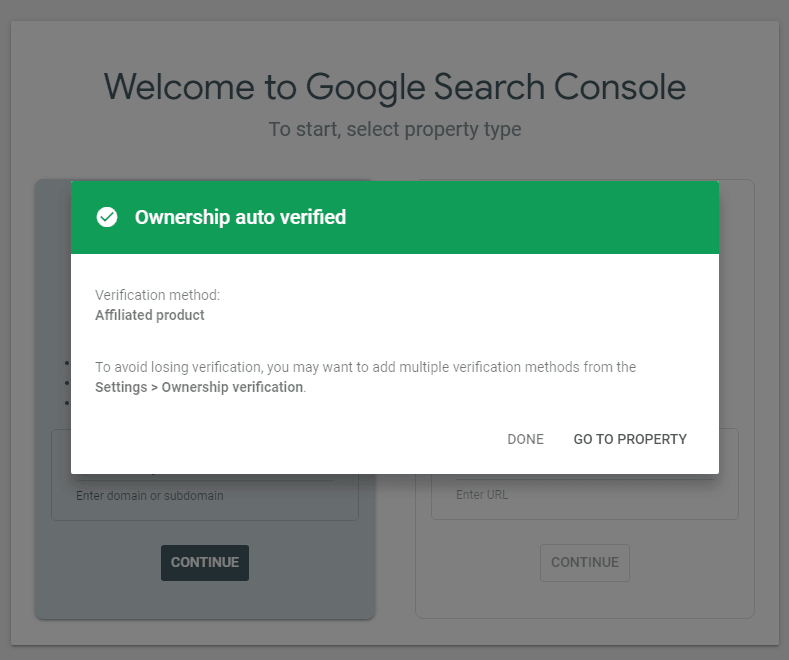
Note : This is an optional approach, if you have registered the domain using Google Domain, verification is automatic in Firebase hosting setup.
Perform the below steps in Firebase console in Hosting page,
Click Add custom domain button and fill in the site name as in the example and click continue.
You will skip section (2) as the site is already verified.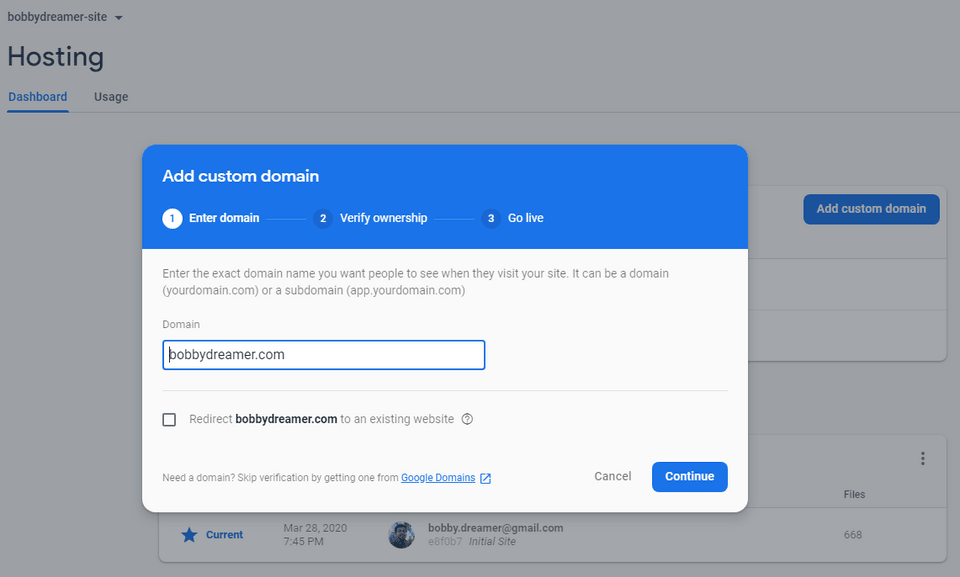
There are two modes either you go with "Quick" or "Advanced"
Quick Mode : You will have to add "A" records to your domain
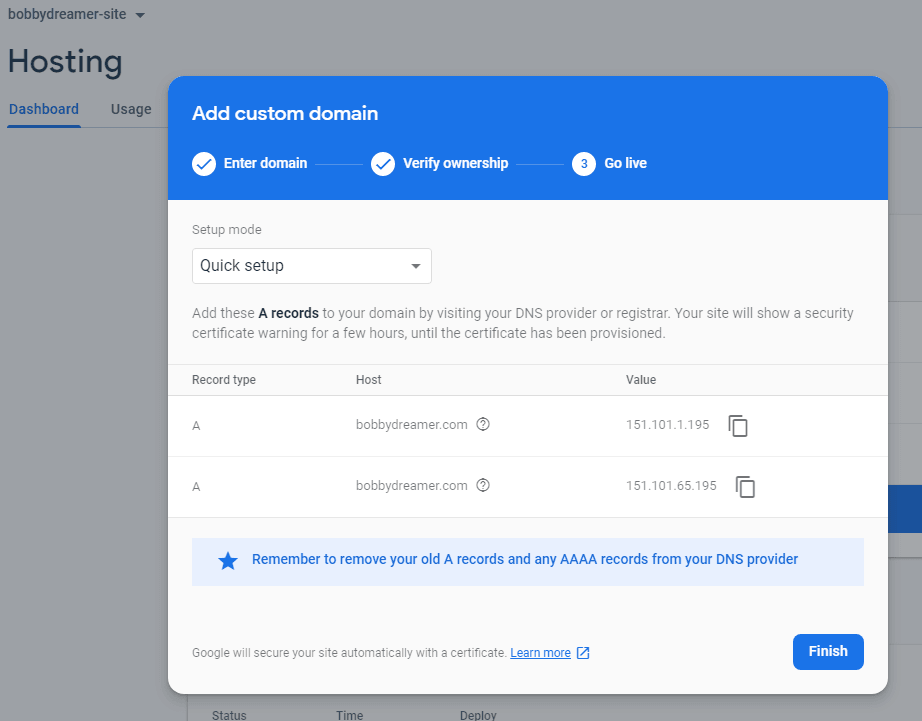
In Google domains, in the name field, you can give either
@as you are setting it up for a root domain or domain name as specified in "Add custom domain box" (ie.,bobbydreamer.com)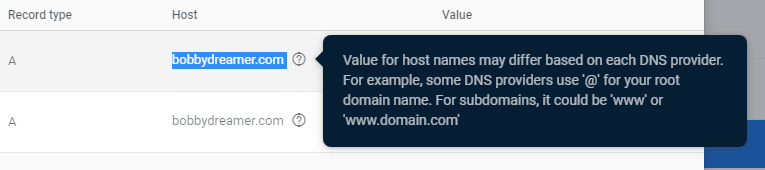
In Google domains, enter the "A" records and click "Add"
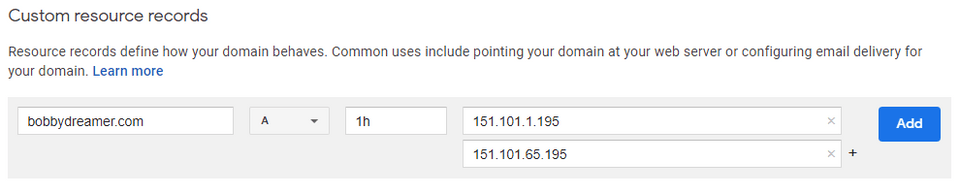
It should appear as below,
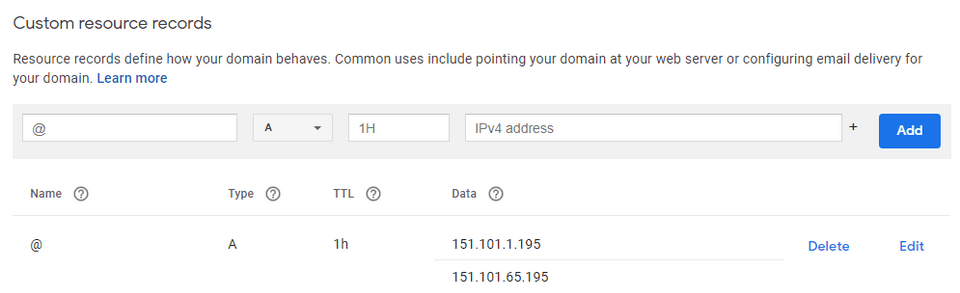
Advanced Mode : You will have to add "TXT" records. Copy & paste from firebase console to DNS provider.
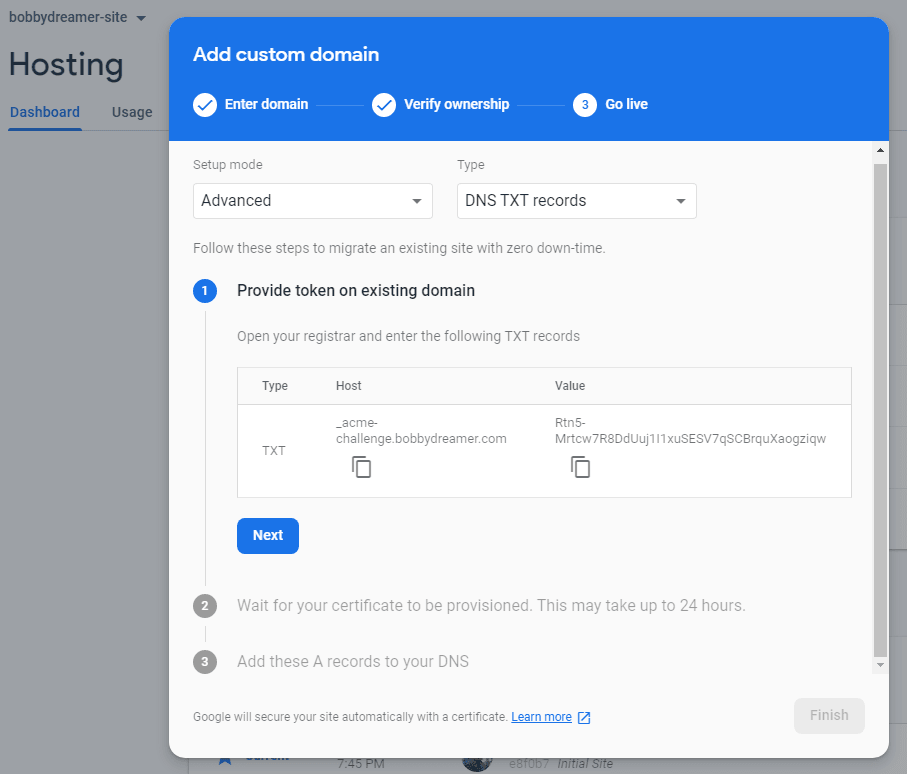
I have already added the "TXT" from Firebase hosting in Google domains, it looks like below(2nd & 3rd record),
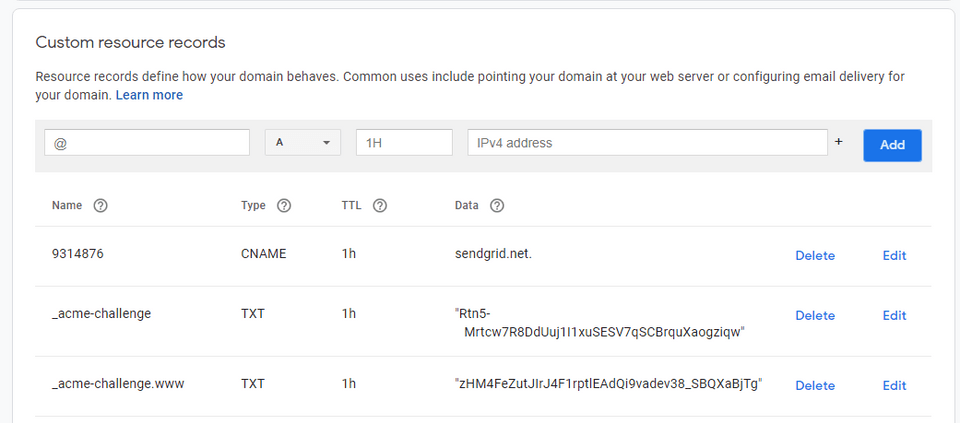
To get to this part, it took 2Hrs
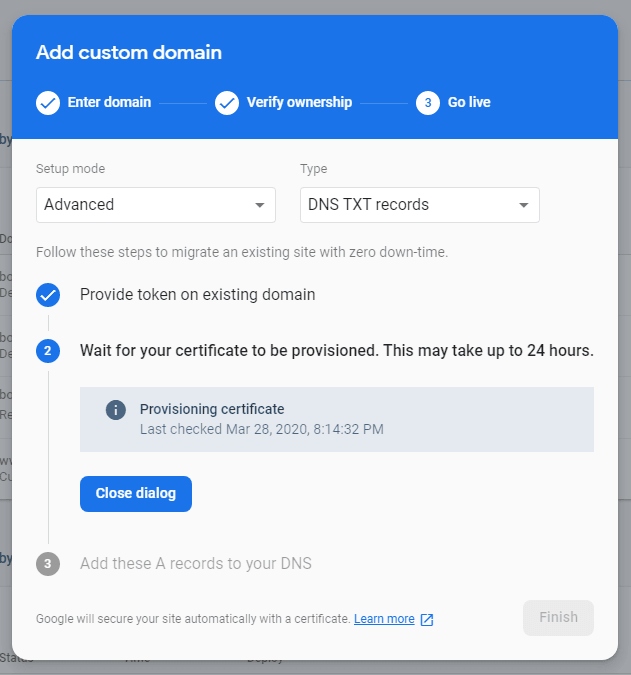
Note : This entire process is a time consuming process, its a wait and watch kind of scenario. For me, "Quick" mode approach was faster(took 2hrs), for you timeframe may vary.
Once the above process is finished, firebase asked me to setup for
www.bobbydreamer.comas initially i had set it up forbobbydreamer.com. Steps are pretty much similar to above and in the end it looked like below in Google Domains
After few mins, i could see the new site
# Next time onwards
Only below commands are required to update content on the site,
1gatsby clean2gatsby build 3gatsby serve 4
5firebase serve --only hosting6firebase deploy -m "New comment"# Next steps
- Make quality content weekly
- Look for a CI/CD approach to build and deploy
- May be, just may be, try to implement the site via App Engine, Kubernetes and Cloud Run
# Technical terms & definitions
Google domains
Resource records : Resource records provide DNS-based information about the hardware and software components that point to and support your domain (hosts, name servers, web servers, email servers).
Each resource record consists of a set of fields:
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A label indicating the name or owner of the record. This can be the root domain (indicated by @) or a subdomain (such as “www”). |
| Type | The record's type. For example, the A (address) record. |
| TTL | (Time-To-Live) How often a copy of the record stored in cache (local storage) must be updated (fetched from original storage) or discarded. Shorter TTLs mean records are fetched more often (access is slower, data is more current). Longer TTLs mean records are fetched from less often (access is faster, data is less current). The default value is 1 hour. Note: When you make changes to a resource record, It could take up to the length of the TTL time for the change to propagate. When you add a new resource record, it will be visible to Internet users in 5 minutes. |
| Data | The record's data, which varies depending on the record's type. For example, a host's IP address for A records. Note that this is the data that is returned during a DNS search. |
Resource Record Types ( some commonly used record types )
In addition to the DNS resource records described here, Google Domains also supports synthetic records that extend the functionality of resource records.A : A (IPv4 address) records map the domain name of a host to the IP address of that host (name-to-address mapping).
1@ A 1h 123.123.123.123Note: A records and AAAA records perform the same function. A records map to IP version 4 (IPv4) addresses. AAAA records map to IP version 6 (IPv6) addresses.
AAAA : AAAA (IPv6 address) records map the domain name of a host to the IP address of that host (name-to-address mapping).
1www AAAA 1h 2002:db80:1:2:3:4:567:89abNote: A records and AAAA records perform the same function. A records map to IP version 4 (IPv4) addresses. AAAA records map to IP version 6 (IPv6) addresses.
CNAME : CNAME (canonical name) records map an alias domain name to a canonical (true) domain name. You can map multiple alias names to the same canonical domain (allowing you to set up A or AAAA record IP addresses in a single location).
In this example, www is the alias domain and example.com is the canonical domain (it's mapped to an IP address using the A record)..
1www CNAME 1h example.com.2example.com. A 1h 123.123.123.123In this example, www and FTP are alias domains and server1.example.com. is the canonical domain (it's mapped to an IP address using the A record).
1www CNAME 1h server1.example.com.2ftp CNAME 1h server1.example.com.3server1.example.com. A 1h 123.123.123.123CNAME records cannot be set for the root domain. Also, the target of a CNAME record can only be a domain name; paths are not allowed. If you want to redirect your root domain, or if your desired target is a URL that includes a path, try one of these options:
- Use the domain forwarding feature instead of a CNAME (see Domain forwarding).
- Create a Forwarding record using the same entries you would put in a CNAME
MX : MX (mail exchange) records map a domain name to a mail server receiving email for that domain. MX records identify which mail servers others use to send email to a domain.
Multiple MX records can be set up for a domain, each with a priority number, where lower numbers have higher priority. In the example below, if mail can't be delivered using the host with the higher priority (10), the host with the lower priority (20) will be used.
1@ MX 1h 10 mailhost1.example.com.2@ MX 1h 20 mailhost2.example.com.If the priority numbers are the same (10 and 10), the MX records can be used to balance the load between hosts; either host will be chosen arbitrarily.
1@ MX 1h 10 mailhost1.example.com.2@ MX 1h 10 mailhost2.example.com.Note: Google Domains does not provide a separate field for the priority number. To specify a priority number, enter the value in the data field followed by the mail host (10 mailhost1.example.com.).
TXT : TXT (text) records contain arbitrary information, in the form of human-readable text or machine-readable data, that can be added to a resource record.
1A TXT 1h ”This is my domain.”
# Resources
- Gatsby : Overview of the Gatsby Build Process
- Gatsby : Deploying to Firebase Hosting
- Firebase : Firebase CLI reference
- Firebase : Connect a custom domain
- Google Domains help