Loading data into BigQuery using Python
— GCP, bigquery, python — 1 min read
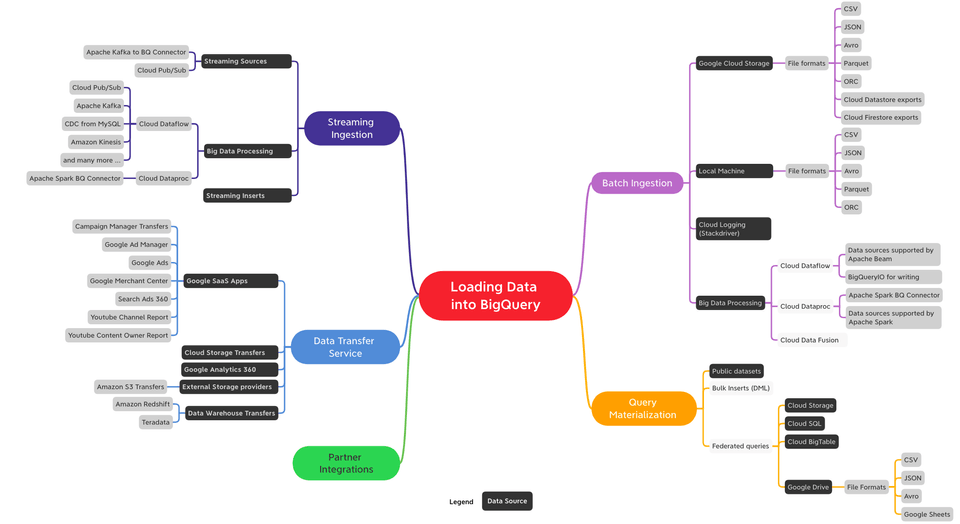
Below picture shows options available to load BigQuery
Below are some sample programs and options which i am using currently or plan to use,
Loading from Local
This program is used to load data in a CSV file extracted from mySQL table into BigQuery. The program does following activities,
- Pre-process(strips spaces) data and saves it in a new file with prefix 'pp-'
- Load data from local into BigQuery
Some Pre-reqs
1import csv2from datetime import datetime3
4from google.cloud import bigquery5
6
7def load_bq(pp_file, table_id, load_type):8
9 with open(pp_file) as f:10 all_cols_from_file = f.readline()11 all_cols_from_file=all_cols_from_file.rstrip('\n').upper().split(',')12 print(all_cols_from_file)13
14 # Construct a BigQuery client object.15 client = bigquery.Client()16
17 # Post-201418 schema = [{'name': 'ts', 'type': 'DATE', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'sc_code', 'type': 'INTEGER', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'sc_name', 'type': 'STRING', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'sc_group', 'type': 'STRING', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'sc_type', 'type': 'STRING', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'open', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'high', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'low', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'close', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'last', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'prevclose', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'no_trades', 'type': 'INTEGER', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'NO_OF_SHRS', 'type': 'INTEGER', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'NET_TURNOVER', 'type': 'NUMERIC', 'mode': 'REQUIRED'}, {'name': 'TDCLOINDI', 'type': 'STRING', 'mode': 'NULLABLE'}, {'name': 'ISIN', 'type': 'STRING', 'mode': 'NULLABLE'}]19
20 job_config = bigquery.LoadJobConfig(21 source_format=bigquery.SourceFormat.CSV, skip_leading_rows=1,22 schema=schema,23 write_disposition=load_type,24 null_marker='\\N' # mySQL marks null value by \N25 )26
27 # Loading CSV file from local system28 with open(pp_file, "rb") as source_file:29 job = client.load_table_from_file(source_file, table_id, job_config=job_config)30
31 # Loading CSV file from GCS32 # uri = "gs://<<bucket-name>>/bse/bhavcopy_csv/EQ_ISINCODE_280921.CSV"33 # job = client.load_table_from_uri(uri, table_id, job_config=job_config) 34
35 job.result() # Waits for the job to complete.36 print(job)37
38 table = client.get_table(table_id) # Make an API request.39 print(40 "Loaded {} rows and {} columns to {}".format(41 table.num_rows, len(table.schema), table_id42 )43 )44
45
46def preprocess_file(input_filename):47 # ---- PreProcess CSV save as new file ----48 temp_folder = '/tmp/'49 ppCSV = temp_folder+'pp-'+input_filename50 with open(input_filename, 'r') as inf, open(ppCSV, 'w', newline='') as of:51 r = csv.reader(inf, delimiter=',')52 w = csv.writer(of, delimiter=',')53 total_rows = 054 for line in r:55 total_rows+=156 trim = (field.strip() for field in line)57 # trim = (field.replace('\\N', '') for field in line) 58 w.writerow(trim) 59
60 return ppCSV61
62
63def main():64
65 input_filename = 'test-bse-data.csv'66 # `<<project-name>>.btd_in3.bse_daily_history`67 table_name = 'bse_daily_history'68 table_id = '{}.{}.{}'.format('<<project-name>>', 'btd_in3', table_name)69
70 pp_file = preprocess_file(input_filename)71 load_bq(pp_file, table_id, 'WRITE_APPEND')72
73
74if __name__ == "__main__":75 main()Input file looks like this
1ts,sc_code,sc_name,sc_group,sc_type,open,high,low,close,last,prevclose,no_trades,NO_OF_SHRS,NET_TURNOVER,TDCLOINDI,ISIN22020-09-08,542963,06AGG,F,Q,0.94,0.94,0.94,0.94,0.94,0.86,1,50,47,\N,INF204KB12L032020-09-08,936963,0ECL21,F,D,1000.00,1000.00,1000.00,1000.00,1000.00,1000.00,1,10,10000,\N,INE804IA718842020-09-08,937079,0EFIL21,F,D,995.00,995.00,995.00,995.00,995.00,992.25,3,25,24875,\N,INE918K07FO152020-09-08,936710,0EFL21A,F,D,1050.10,1099.90,1050.10,1099.90,1099.90,1099.90,2,11,11600,\N,INE804IA707162020-09-08,936720,0EFL24,F,D,940.00,940.00,920.00,920.00,920.00,945.00,29,2055,1891480,\N,INE804IA712172020-09-08,935790,0EHFL26,F,D,738.00,738.00,738.00,738.00,738.00,918.80,1,1,738,\N,INE530L0723682020-09-08,936508,0ICFL24,F,D,925.10,925.10,800.05,900.00,900.00,999.95,5,135,123960,\N,INE614X07092Command used to unload data from mySQL is below, first select is header and second is the SQL to select data.
1select * from (2select 'ts', 'sc_code', 'sc_name', 'sc_group', 'sc_type', 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close', 'last', 'prevclose', 'no_trades', 'NO_OF_SHRS', 'NET_TURNOVER', 'TDCLOINDI', 'ISIN'3union all 4select date(ts) ts, sc_code, sc_name, sc_group, sc_type, open, high, low, close, last, prevclose, no_trades, NO_OF_SHRS, NET_TURNOVER, TDCLOINDI, ISIN from bse_daily_history)a5INTO OUTFILE 'D:/BigData/12. Python/1. Tryouts/GCP/OTLs-BQ/bse-2014-2020.csv' FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n' ;Another interesting thing in the above program is the specification of BigQuery Schema. Below query is used to extract the mySQL column information.
1SELECT COLUMN_NAME, 2CASE3 WHEN data_type = 'datetime' then "DATE"4 WHEN data_type = 'bigint' then "INTEGER"5 WHEN data_type = 'varchar' then "STRING"6 WHEN data_type = 'decimal' then "NUMERIC"7 WHEN data_type = 'char' then "STRING"8END as BQ_DATA_TYPE, 9CASE10 WHEN IS_NULLABLE = 'NO' then "REQUIRED"11 WHEN IS_NULLABLE = 'YES' then "NULLABLE"12END as BQ_MODE13 FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS14 WHERE table_name = 'bse_daily_history'15 AND table_schema = 'test'16INTO OUTFILE 'D:/BigData/12. Python/1. Tryouts/GCP/OTLs-BQ/schema-bse_daily_history.txt' FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n' ;Output to the above SQL looks like this
1ts,DATE,REQUIRED2sc_code,INTEGER,REQUIRED3sc_name,STRING,REQUIRED4sc_group,STRING,REQUIRED5sc_type,STRING,REQUIRED6open,NUMERIC,REQUIRED7high,NUMERIC,REQUIRED8low,NUMERIC,REQUIRED9close,NUMERIC,REQUIRED10last,NUMERIC,REQUIRED11prevclose,NUMERIC,REQUIRED12no_trades,INTEGER,REQUIRED13NO_OF_SHRS,INTEGER,REQUIRED14NET_TURNOVER,INTEGER,REQUIRED15TDCLOINDI,STRING,NULLABLE16ISIN,STRING,NULLABLEAbove file is read by the below python program to generate array of dictionary objects.
1# BigQuery Schema Generator2
3import csv4
5arr = []6with open("schema-bse_daily_history.txt", "r") as f:7 reader = csv.reader(f, delimiter=",") 8 for i, line in enumerate(reader):9 dict = {}10 print('line[{}] = {}'.format(i, line)) 11 dict['name'] = line[0]12 dict['type'] = line[1]13 dict['mode'] = line[2]14 arr.append(dict)15
16print(arr)Loading from GCS
Loading BigQuery from GCS isn't much different when comparing loading from local file. In the earlier program uncommenting below lines enables it load data from GCS. Thats pretty much it.
1# Loading CSV file from GCS2 uri = "gs://<<bucket-name>>/bse/bhavcopy_csv/EQ_ISINCODE_280921.CSV"3 job = client.load_table_from_uri(uri, table_id, job_config=job_config)Loading a Dataframe
This program uses an external library pandas_gbq to load BigQuery
Program does the following,
- Extracts date from filename
- Reads the CSV file to get all the header columns
- Pandas dataframe uses only only few specific column mentioned in variable
bse_csv_columns - Adds a new date object column to dataframe
- Finally data is loaded into BQ
1# Default Installs2import os3import pandas as pd4from datetime import datetime5import pandas_gbq6
7# Functions8
9# Formatting Date10get_datetime = lambda s: datetime.strptime(s, '%d%m%y').date()11
12def csv_to_df(filename):13 """14 Read BSE Daily csv file and return dataframe15
16 :param filename: CSV Filename17 """18
19 date = get_datetime(filename[-10:-4])20 print(date)21
22 with open(filename) as f:23 all_cols_from_file = f.readline()24 all_cols_from_file=all_cols_from_file.upper().split(',')25 # print(all_cols_from_file)26
27 # Columns28 # SC_CODE,SC_NAME,SC_GROUP,SC_TYPE,OPEN,HIGH,LOW,CLOSE,LAST,PREVCLOSE,NO_TRADES,NO_OF_SHRS,NET_TURNOV,TDCLOINDI,ISIN_CODE,TRADING_DATE,FILLER2,FILLER329
30 bse_csv_columns = ["SC_CODE","SC_NAME","SC_GROUP","SC_TYPE"31 ,"OPEN","HIGH","LOW","CLOSE","LAST","PREVCLOSE"32 ,"NO_TRADES","NO_OF_SHRS","NET_TURNOV","TDCLOINDI","ISIN_CODE"]33
34 df_bse_daily = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), filename), sep=','35 , names=all_cols_from_file36 , usecols=bse_csv_columns37 ,skiprows=138 ,dtype=object39 ,skip_blank_lines=True)40
41 # df_bse_daily['TS'] = date 42
43 print(df_bse_daily.info())44
45 return df_bse_daily46
47def load_bigquery(df):48 pandas_gbq.to_gbq(49 df, 'BTD_20210925.bse_daily_str', project_id='<<project-name>>', if_exists='replace')50
51
52def main():53 print('getcwd : ', os.getcwd())54
55 df = csv_to_df('EQ_ISINCODE_010119.CSV')56 # print(df.columns)57 # print(df.head())58
59 load_bigquery(df)60
61
62if __name__ == "__main__":63 main()Input file looks like this
1SC_CODE,SC_NAME,SC_GROUP,SC_TYPE,OPEN,HIGH,LOW,CLOSE,LAST,PREVCLOSE,NO_TRADES,NO_OF_SHRS,NET_TURNOV,TDCLOINDI,ISIN_CODE,TRADING_DATE,FILLER2,FILLER32500002,ABB LTD. ,A ,Q,1318.20,1338.75,1312.55,1320.40,1323.55,1332.00,255,1816,2407362.00,,INE117A01022,01-Jan-19,,3500003,AEGIS LOGIS ,A ,Q,204.75,205.70,200.60,203.90,203.90,204.20,294,5672,1150504.00,,INE208C01025,01-Jan-19,,4500008,AMAR RAJA BA,A ,Q,743.45,747.50,737.60,739.65,739.65,742.75,253,7307,5424260.00,,INE885A01032,01-Jan-19,,5500009,A.SARABHAI ,X ,Q,13.60,13.75,13.00,13.43,13.44,13.24,41,12887,172463.00,,INE432A01017,01-Jan-19,,6500010,HDFC ,A ,Q,1973.55,2018.60,1956.00,2009.60,2009.60,1970.00,2531,320697,630395875.00,,INE001A01036,01-Jan-19,,Loading a JSON
Loading newline delimited JSON file from Cloud Storage
This is pretty much straight forward, its a from google samples to load json data from Cloud Storage
1# Load JSON from Cloud Storage to BQ2import io3from google.cloud import bigquery4
5# Construct a BigQuery client object.6client = bigquery.Client()7
8# TODO(developer): Set table_id to the ID of the table to create.9table_id = "<<project-name>>.test_public_data.us_states_jl"10
11job_config = bigquery.LoadJobConfig(12 write_disposition=bigquery.WriteDisposition.WRITE_TRUNCATE,13 source_format=bigquery.SourceFormat.NEWLINE_DELIMITED_JSON,14 schema=[15 bigquery.SchemaField("name", "STRING"),16 bigquery.SchemaField("post_abbr", "STRING"),17 ],18)19
20uri = "gs://cloud-samples-data/bigquery/us-states/us-states.json"21load_job = client.load_table_from_uri(22 uri, table_id, job_config=job_config23) # Make an API request.24
25load_job.result() # Waits for the job to complete.26
27destination_table = client.get_table(table_id)28assert destination_table.num_rows > 029print("Loaded {} rows.".format(destination_table.num_rows))Input file looks like this,
1{"name": "Alabama", "post_abbr": "AL"}2{"name": "Alaska", "post_abbr": "AK"}3{"name": "Arizona", "post_abbr": "AZ"}4{"name": "Arkansas", "post_abbr": "AR"}Loading from Local json file
Same input file as above but from local
1# Load JSON from local to BQ2
3import io4from google.cloud import bigquery5
6# Construct a BigQuery client object.7client = bigquery.Client()8
9# TODO(developer): Set table_id to the ID of the table to create.10filename = 'us-states.json'11table_id = "<<project-name>>.test_public_data.us_states_jl"12
13job_config = bigquery.LoadJobConfig(14 schema=[15 bigquery.SchemaField("name", "STRING"),16 bigquery.SchemaField("post_abbr", "STRING"),17 ],18 source_format = bigquery.SourceFormat.NEWLINE_DELIMITED_JSON,19)20
21with open(filename, "rb") as source_file:22 job = client.load_table_from_file(source_file, table_id, job_config=job_config).result()23
24assert job.output_rows > 025
26print("Loaded {} rows into {}".format(job.output_rows, table_id))Loading newline delimited JSON file from Pandas
In this example, dataframe is converted into JSON object and loaded
1# Load JSON data from Pandas to BigQuery2
3import pandas as pd4import numpy as np5from google.cloud import bigquery6import os, json7
8### Converts schema dictionary to BigQuery's expected format for job_config.schema9def format_schema(schema):10 formatted_schema = []11 for row in schema:12 formatted_schema.append(bigquery.SchemaField(row['name'], row['type'], row['mode']))13 return formatted_schema14
15### Create dummy data to load16df = pd.DataFrame([[2, 'Jane', 'Doe']],17columns=['id', 'first_name', 'last_name'])18
19### Convert dataframe to JSON object20json_data = df.to_json(orient = 'records')21print(json_data)22json_object = json.loads(json_data)23
24### Define schema as on BigQuery table, i.e. the fields id, first_name and last_name 25table_schema = {26 'name': 'id',27 'type': 'INTEGER',28 'mode': 'REQUIRED'29 }, {30 'name': 'first_name',31 'type': 'STRING',32 'mode': 'NULLABLE'33 }, {34 'name': 'last_name',35 'type': 'STRING',36 'mode': 'NULLABLE'37 }38
39project_id = '<<project-name>>'40dataset_id = 'test_public_data'41table_id = 'test_jsonload'42
43client = bigquery.Client(project = project_id)44dataset = client.dataset(dataset_id)45table = dataset.table(table_id)46
47job_config = bigquery.LoadJobConfig()48job_config.source_format = bigquery.SourceFormat.NEWLINE_DELIMITED_JSON49
50job_config.schema = format_schema(table_schema)51print(job_config.schema)52
53# Default is append54job = client.load_table_from_json(json_object, table, job_config = job_config).result()55
56destination_table = client.get_table('{}.{}.{}'.format(project_id, dataset_id, table_id))57print("Loaded {} rows.".format(destination_table.num_rows))